
Makati
Philippines
Phone Number
0962 950 7814
(02) 8637-2360
Send Your Mail
slcelitemedicalcare@gmail.com

Philippines
0962 950 7814
(02) 8637-2360
slcelitemedicalcare@gmail.com
MSCs are multipotent stem cells with the unique ability to: Transform into bone, cartilage, muscle, or fat cells Reduce inflammation and modulate the immune system Release healing factors that repair damaged tissues.
Using Youngest and Most Potent MSCs from: |
Clinical Applications |
|
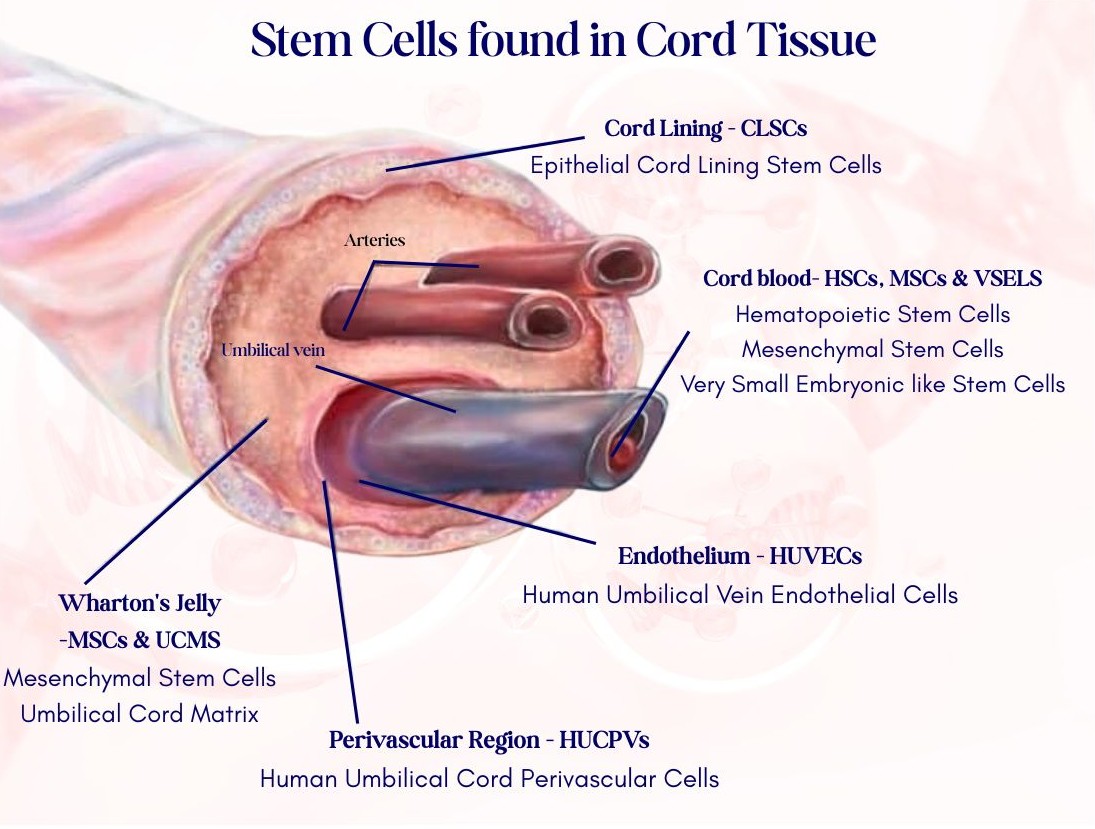
Wharton’s Jelly (Umbilical Cord Tissue) Highest concentration of primitive MSCs Umbilical Cord Blood Rich in growth factors |
→ Joint & Cartilage Repair → Neurological Conditions → Autoimmune Diseases → Anti-Aging & Wellness |
Ethically Sourced: Collected from donated cords after healthy births (no harm to mother or baby)
Biologically Superior: Faster growth & stronger regenerative potential than adult-derived MSCs
Safe & Effective: No rejection risk due to immune-privileged properties
|
Feature |
Advantages |
Clinical Benefit |
Multipotent Differentiation |
Can turn into Bone, Cartilage, Fat, Muscle Cells. |
Repairs damaged tissues (e.g., osteoarthritis). |
Immunomodulation |
Reduces Inflammation & Immune Overreaction. |
Treats autoimmune diseases (e.g., Crohn’s). |
Trophic Effects |
Releases growth factors (VEGF, IGF-1) to heal nearby cells. |
Accelerates wound healing & organ repair. |
Low Immunogenicity |
Rarely rejected (even from donors). |
No need for perfect donor matches. |
Easy Sourcing |
Isolated from bone marrow, fat, umbilical cord. |
Minimally invasive harvesting (e.g., liposuction). |
Safety Profile |
No ethical concerns (adult-derived, not embryonic). |
FDA-approved for certain conditions. |
Anti-Fibrotic |
Prevents scar tissue formation. |
Improves recovery after heart/liver injury. |
Targeted Homing |
Migrates to injured areas when injected. |
Delivers therapy precisely to damaged sites. |
|
Name |
Indications |
Mechanism of action |
Course |
Expected Outcomes |
|
MSC Complex Stem Cells |
Common signs of skin aging and damage include slower cell renewal, redness, poor circulation, loss of firmness, enlarged pores, fine lines, dark spots, dryness, dullness, sun damage, thinning skin, hormonal breakouts, and stubborn scars. |
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are powerful, versatile cells with unique healing abilities. Unlike typical stem cells, they can regulate the immune system, reduce cell death, provide nourishment, and release healing factors that improve the cellular environment. These factors help reduce inflammation, repair damage, and promote local tissue renewal—key to restoring healthy, youthful skin. |
30 million cells per dose, enriched with over 140 bioactive factors. Administered once every 30 days for 3 consecutive sessions per treatment course. For sustained efficacy, patients may repeat one course annually. |
Post-treatment evaluation shows measurable improvements in skin elasticity, texture, and tone, with a marked reduction in visible aging markers. Optimal results are maintained with annual courses. |
|
MSC Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
Aging and stress often bring fatigue, insomnia, poor appetite, frequent colds, irritability, constipation, and heart palpitations—all signs your body needs support. |
Stem cells naturally maintain tissue health through self-renewal and differentiation, balancing regeneration and decline. However, aging significantly reduces both stem cell quantity and activity, leading to tissue degeneration and disease. Stem cell therapy addresses this by repairing damaged cells, activating dormant cells, increasing healthy cell populations, and enhancing cellular function – effectively preventing cell aging to treat diseases and delay aging at their root cause. |
Each course delivers 80 million cells across 3 sessions (administered bi-weekly). After 1-2 months of evaluation, patients with positive outcomes may repeat one course annually for continued benefits. |
Youthful vitality brings marked improvements in quality of life – evidenced by better sleep quality, enhanced physical stamina, reduced fatigue, improved appetite, optimized organ function, lowered mental stress, and superior blood circulation. These systemic upgrades work synergistically to restore peak physiological performance. |
|
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
Bone Damage, Degenerative Arthritis, Knee Soft Tissue Injury, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Etc. |
Stem cell transplantation repairs and replaces damaged cells and tissues, as the implanted stem cells differentiate into the appropriate cell types based on the local microenvironment. Additionally, stem cells can differentiate into immune cells, helping to restore and regulate the immune system while suppressing excessive T-cell activity. Once activated, they secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines that reduce tissue damage in bones, joints, and synovium, effectively slowing disease progression. |
The treatment involves injecting 20 million cells directly into the affected joint, administered once monthly for 3-4 sessions per course. |
Most patients report less pain, better movement, and reduced swelling after just 3-4 monthly injections. Follow-up tests show many achieve complete remission of rheumatoid markers. |
|
Diabetic Islet Repair Stem Cells |
Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Complications Of Diabetes |
Stem cell therapy addresses type 2 diabetes through three key mechanisms: (1) direct differentiation into functional insulin-secreting cells, (2) regeneration and repair of pancreatic β-cells to restore endogenous insulin production, and (3) metabolic modulation via NLRP3 inflammasome downregulation in liver/adipose tissue coupled with PI3K-AKT pathway activation – collectively improving β-cell function while ameliorating insulin resistance. |
The treatment protocol involves intravenous infusion of 80 million cells per bag, administered every 7-15 days for a total of 4-6 sessions per course. |
Within about 3 weeks of treatment, most patients see significant blood sugar improvements (20-50% lower), with lab tests confirming better natural insulin production as the pancreas begins to heal. |
|
Neural Stem Cells |
Stem cell treatments may help with brain and nerve conditions like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, memory problems, sleep issues, and recovery from stroke or brain bleeding damage. |
Stem cells help heal nerve damage by protecting and repairing brain cells, nourishing damaged areas, reducing harmful inflammation, improving blood flow to injured tissue, and creating a healthier environment for recovery. |
The treatment regimen consists of 3-4 courses administered every 15-30 days, with each course containing 80 million cells per infusion bag. Additionally, patients receive 1-2 doses of CIK therapy at 5 billion cells per dose. |
Patients often experience better sleep, sharper memory, and clearer thinking. For nerve damage recovery, many regain strength in their arms and legs, become more independent with daily activities, and enjoy a better quality of life. |
|
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
Acute And Chronic Hepatitis, Viral Hepatitis, Fatty Liver, Chronic Liver Tissue Damage |
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) exerts multifaceted therapeutic effects on liver repair by: (1) activating hepatic stem cells to drive hepatocyte proliferation and regeneration; (2) suppressing stellate cell activation to rebalance collagen turnover, thereby counteracting fibrosis; (3) enhancing metabolic efficiency of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins; (4) stimulating angiogenesis in damaged liver tissue; (5) secreting matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to degrade pathological extracellular matrix deposits in fibrotic/cirrhotic livers; and (6) modulating immune cell infiltration and systemic inflammatory responses to mitigate further hepatic injury. |
The treatment regimen consists of 4-6 intravenous infusions administered every 7-10 days, with each infusion containing 80 million cells per bag |
Patients demonstrated significant improvement in liver function markers within two weeks of treatment initiation. At the one-month follow-up evaluation, objective measures including bilirubin levels (reflected in reduced skin/mucosal jaundice) and subjective indicators (appetite restoration and mental status improvement) showed marked enhancement compared to baseline. |
|
Chronic Kidney Disease-Directed Functional Stem Cells |
Acute And Chronic Nephritis |
Stem cell therapy improves renal function through three key mechanisms: (1) enhancing renal microcirculation to reduce glomerular hypertension and alleviate ischemia-hypoxia, thereby restoring systemic blood flow; (2) stimulating erythropoietin secretion from renal cells to boost red blood cell production and correct anemia; and (3) modulating immune responses through differentiation into regulatory immune cells, which rebalances the immune system and promotes kidney tissue repair. |
The number and frequency are determined according to the physical condition |
1. Delay The Progression of the Disease. |
|
Amniotic Stem Cells |
Premature Ovarian Failure, Endometrial Damage, External Vaginal Sensitivity, And Sexual Dysfunction in Women. |
Stem cell therapy promotes ovarian repair through multiple synergistic actions: (1) paracrine secretion of cytoprotective factors that inhibit apoptosis and regenerate damaged cells; (2) direct engraftment and differentiation at injury sites to functionally replace compromised tissue; (3) immunomodulation that dampens excessive immune responses while activating endogenous repair pathways; (4) anti-fibrotic effects that preserve ovarian stroma architecture; (5) vascular niche support via differentiation into endothelial progenitors; and (6) epigenetic reprogramming of ovarian cells to restore physiological function. |
The combined treatment protocol consists of: (1) intravenous administration of 80 million functionally-enhanced cells per infusion for 4-6 sessions, and (2) direct bilateral ovarian injections of 20 million cells per ovary per session. This dual-route approach demonstrates synergistic efficacy for ovarian functional restoration. |
1. The ovarian function is restored, ovulation is restored, and the number of follicles increases significantly, which can lay the foundation for the success of IVF. |
|
Kidney Function Stem Cells |
Targets inflammatory (prostatitis), functional (sexual dysfunction/premature ejaculation), and hormonal (androgen deficiency) aspects of male reproductive health, while implementing preventive strategies against BPH and prostate carcinogenesis. |
Stem cell therapy regenerates youthful kidney cells and testicular stromal cells, which: (1) replace damaged renal cells to restore kidney function and improve lower limb circulation, and (2) boost testosterone production and spermatogenesis in the testes—collectively enhancing physiological responses, correcting dysfunction, and elevating male vitality and quality of life. |
The treatment regimen consists of 4-6 intravenous infusions administered every 7-10 days, with each infusion containing 80 million cells per bottle. |
Following autologous mesenchymal stem cell therapy, patients demonstrated statistically significant improvements in both standardized metrics – the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-15) scores increased by [X] points (p<0.01) and Erectile Hardness Scale (EHS) grades improved from baseline, reflecting enhanced erectile function, restored libido, and greater sexual satisfaction. |
|
Autologous Cells Are Immune To CIK Cells |
Chronic inflammation driven by senescent cell accumulation disrupts normal cell cycle regulation, accelerating aging, tissue damage, and precancerous changes. This process contributes to age-related pathologies including atherosclerosis, fibrosis, and cancer—particularly in immunocompromised individuals with diminished viral and tumor surveillance capabilities. |
This immunotherapy involves isolating a patient’s immune cells, expanding them exponentially through in vitro cultivation to enhance their targeted cytotoxic capabilities, and reinfusing them to systematically eliminate pathogens, malignant cells, and aberrant mutations—simultaneously overcoming immune tolerance while activating robust, long-lasting immune surveillance for combined therapeutic and prophylactic benefits. |
The treatment regimen consists of 3 intravenous infusions administered every 15-30 days, with each infusion containing 5 billion cells per bag. |
This therapy promotes immune system reconstitution, enhancing overall immune competence while strengthening antiviral defenses and anti-tumor surveillance capabilities. |
|
Cord Blood Multifactor Activation |
This treatment addresses: (1) chronic gastrointestinal dysfunction presenting with persistent appetite loss, dizziness, and fatigue; (2) immune-compromised individuals with prolonged malaise and benign proliferative conditions (cysts/nodules); and (3) patients suffering recurrent inflammatory disorders including gastroenteritis, respiratory infections (pneumonia/rhinitis), and chronic dermatological conditions (eczema/dermatitis). |
(1) Multifactor-activated immune T cells can secrete cytotoxins: perforin, granzyme, etc., carry out exocytosis destruction on the closed cell membrane of target cells (mutant cells, aging cells, necrotic cells, infected cells, etc.), realize the lysis of abnormal cells, and reflect the inherent function of killer T cells – to remove senescent, necrotic and mutated cells. (2) Multifactor-activated immune T cells secrete IFN-γ, GM-CSF, IL-23, IL-3 and other cytokines to regulate immune balance, activate the body’s immune system, and improve the body’s immune function. (3) Contains umbilical cord blood stem cells with anti-aging effect and repairs body damage. |
The recommended immune-boosting regimen consists of 1-2 annual treatment courses, each delivering 21 billion activated T cells via intravenous infusion over 7 days, with a minimum 3-month interval between courses. |
This therapy enhances immune competence and hematopoietic activity, optimizing the metabolic turnover of leukocytes, erythrocytes, and thrombocytes to sustain hematological health. By improving circulatory efficiency and systemic metabolism, it mitigates subclinical dysfunction and reduces disease susceptibility. |
|
Activate PD-1-T Cells |
Following chemoradiotherapy, treatment discontinuation often becomes necessary due to severe cytopenia (leukopenia/thrombocytopenia). Subsequent surgical tumor resection addresses macroscopic disease while adjuvant therapies target residual micrometastases and circulating tumor cells. |
Activated PD-1-T cells combat cancer through multiple synergistic mechanisms: (1) Direct tumor cell lysis via perforin/granzyme exocytosis, penetrating and disrupting cancer cell membranes; (2) Induction of apoptotic signaling through cytotoxic cytokines; (3) Secretion of immunomodulatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-11, IL-23) to restore immune balance and enhance systemic antitumor responses; and (4) Execution of canonical cytotoxic T-cell functions—eliminating senescent, necrotic, and genetically aberrant cells to maintain tissue homeostasis. |
The adjuvant immunotherapy regimen consists of 3-6 treatment courses (dose-adjusted based on disease status), with each course delivering 21 billion cellular units via 7-day continuous IV infusion. A minimum 14-day interval is required between courses to monitor response and ensure safety. |
Immunotherapy demonstrates measurable therapeutic effects through: (1) declining tumor markers (CEA, AFP, CA199, etc.), indicating reduced tumor burden or activity; (2) radiologically confirmed shrinkage of primary lesions/metastatic lymph nodes; (3) rapid hematopoietic recovery with elevated WBC/platelet counts; (4) improved quality of life (reduced pain, gastrointestinal toxicity, fatigue; better sleep/appetite); (5) resolution of malignant effusions (pleural/ascites); (6) enhanced immune competence; and (7) systemic benefits including regression of benign nodules, skin revitalization (reduced pigmentation/psoriasis), and alleviation of comorbid conditions like arthralgia. |
|
CAR-NK Cells |
This therapy is indicated for: (1) individuals with active viral infections, (2) oncology patients undergoing treatment, and (3) post-operative tumor resection cases requiring immune reconstitution. |
Natural Killer (NK) cell activity serves as a key biomarker for assessing the body’s ability to combat tumors and viral infections. Patients with hematologic malignancies, solid tumors, immunodeficiency disorders (including AIDS), and certain viral infections typically exhibit reduced NK cell function. Conversely, elevated NK activity is observed in host-versus-graft responses. As granular lymphocytes of the innate immune system, NK cells mediate rapid cytotoxicity against tumor cells through direct lysis. |
The treatment protocol consists of 3 intravenous infusions per therapeutic course, with each infusion containing 50 billion cellular units. |
This therapy enables targeted identification and destruction of malignant cells and virally-infected host cells through antigen-specific recognition mechanisms. |
|
CAR-T Cells |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), |
CAR-T therapy utilizes genetic engineering to equip a patient’s T cells with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), enabling them to precisely identify and eliminate cancer cells. These modified CAR-T cells are expanded in vitro before reinfusion, enhancing both tumor-targeting specificity and cytotoxic activation against malignancies. |
It depends on the physical condition |
Activates T cells to kill cancer cells |
|
HPV-positive Targets Immune Cell HCTLs |
Diseases of the Skin and Mucous Membranes of the Reproductive System (HPV-16, 18, 33, 52, 58, Etc.) and Related Tumors Such as Cervical Cancer, Rectal Cancer, Oral Cancer, Breast Cancer, Penile Cancer, Anal Cancer and Tonsillar Tumors; |
Tumor cells express unique antigens that can be targeted through genetic engineering. By isolating a patient’s immune cells and stimulating them ex vivo with recombinant vectors encoding tumor antigen genes, we generate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) capable of precisely recognizing and eliminating malignant cells while sparing healthy tissues. |
1. Viral Infection Patients: Patients receive monthly CTL infusions over a three-month course. Treatment continuation is recommended if clinical improvement or disease stabilization is observed. 2. Early-Stage Tumor Patients (Stage I-II): 3. Advanced-Stage Tumor Patients (Stage III-IV): 4. Post-Chemo/Radiotherapy Patients: |
Treatment outcomes are personalized based on individual health status and diagnostic evaluations. For HPV-positive patients, viral clearance (conversion to negative status) is typically achieved within six months of therapy. In advanced cancer cases, this regimen can induce metastatic regression, significantly improve quality of life, and extend survival by 5-10 years. |