
Makati
Philippines
Phone Number
0962 950 7814
(02) 8637-2360
Send Your Mail
slcelitemedicalcare@gmail.com

Philippines
0962 950 7814
(02) 8637-2360
slcelitemedicalcare@gmail.com
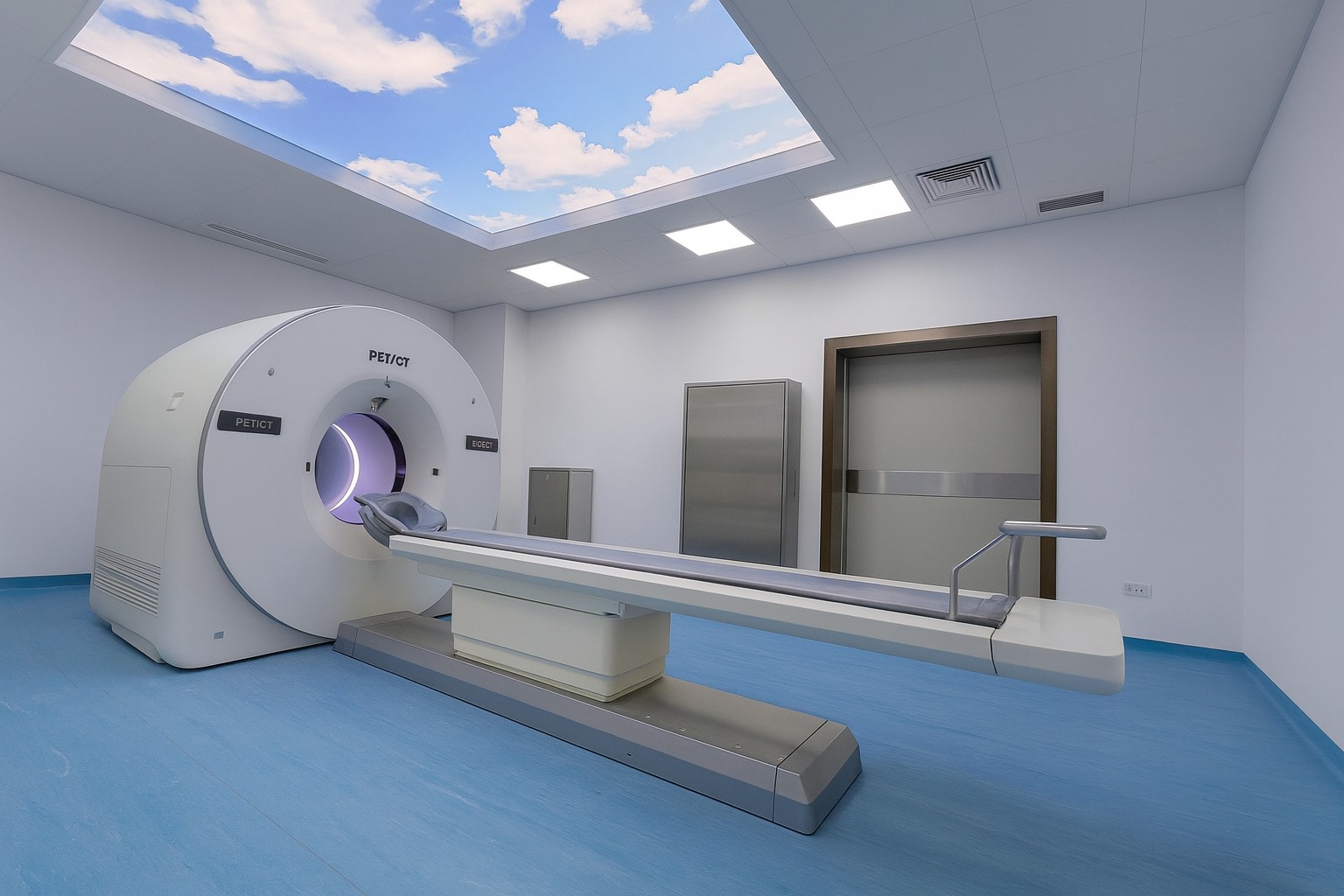
A PET-CT (Positron Emission Tomography – Computed Tomography) system is an advanced medical imaging technology that combines two scanning techniques to provide detailed information about both structure (anatomy) and function (metabolism) in a single scan.
How It Works:
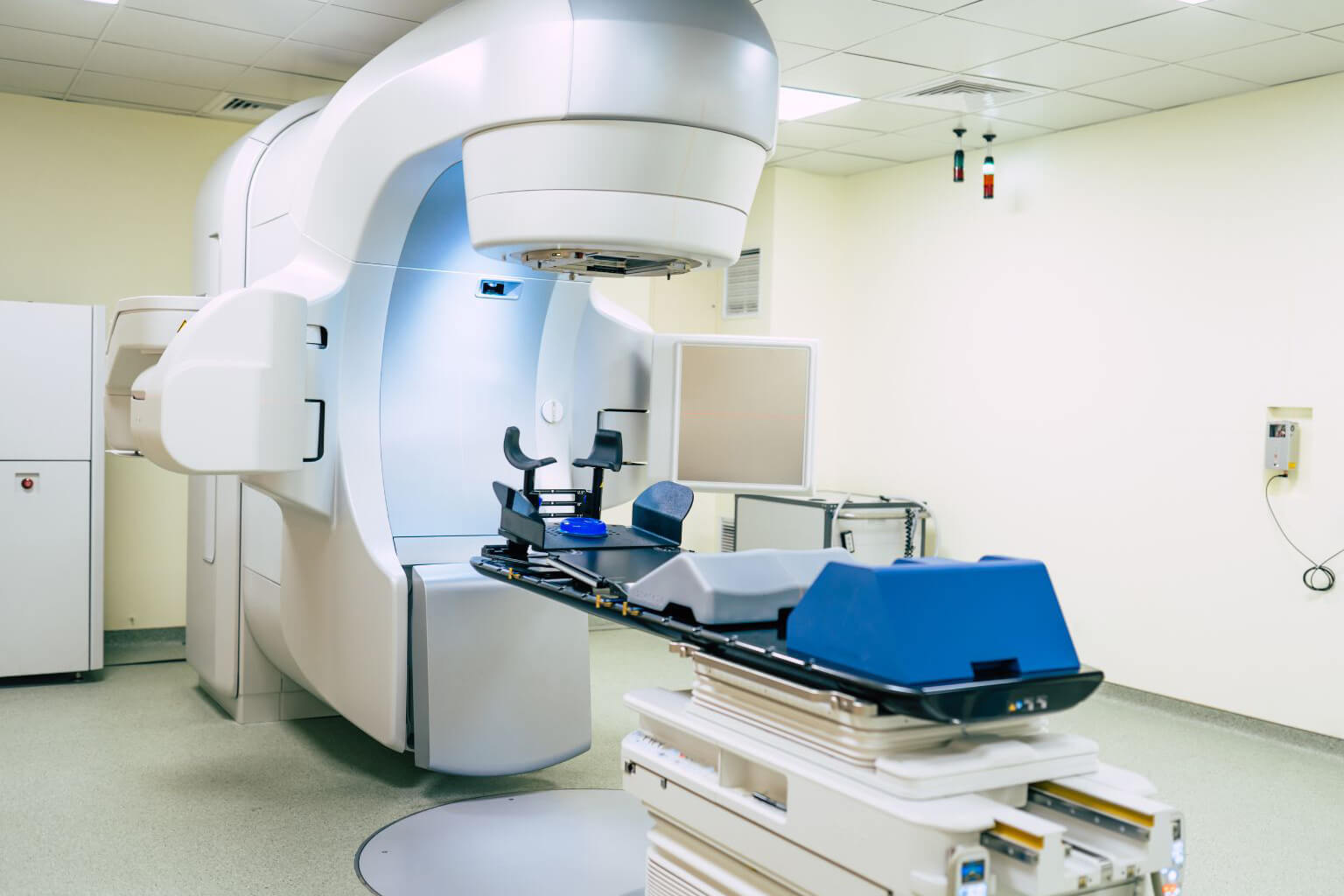
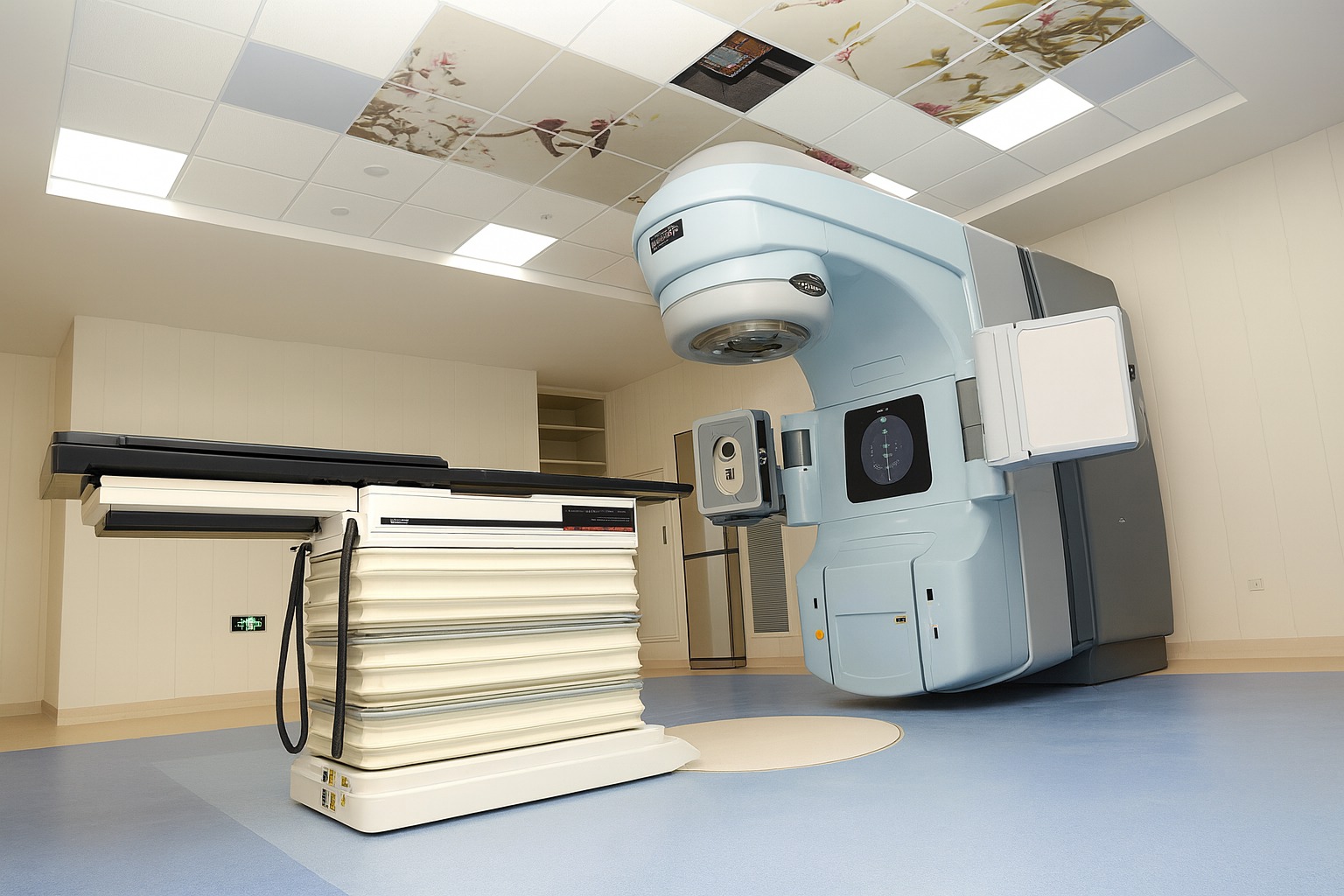
A Linear Accelerator (LINAC) is the most advanced and widely used radiotherapy system for treating cancer. It delivers high-energy X-rays or electrons precisely to tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
How a LINAC Works:
A 3.0 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) system is a high-field, advanced medical imaging device that uses powerful magnetic fields (twice as strong as standard 1.5T MRI) and radio waves to produce exceptionally detailed, high-resolution images of the body’s internal structures without radiation.
Key Features of 3.0T MRI:
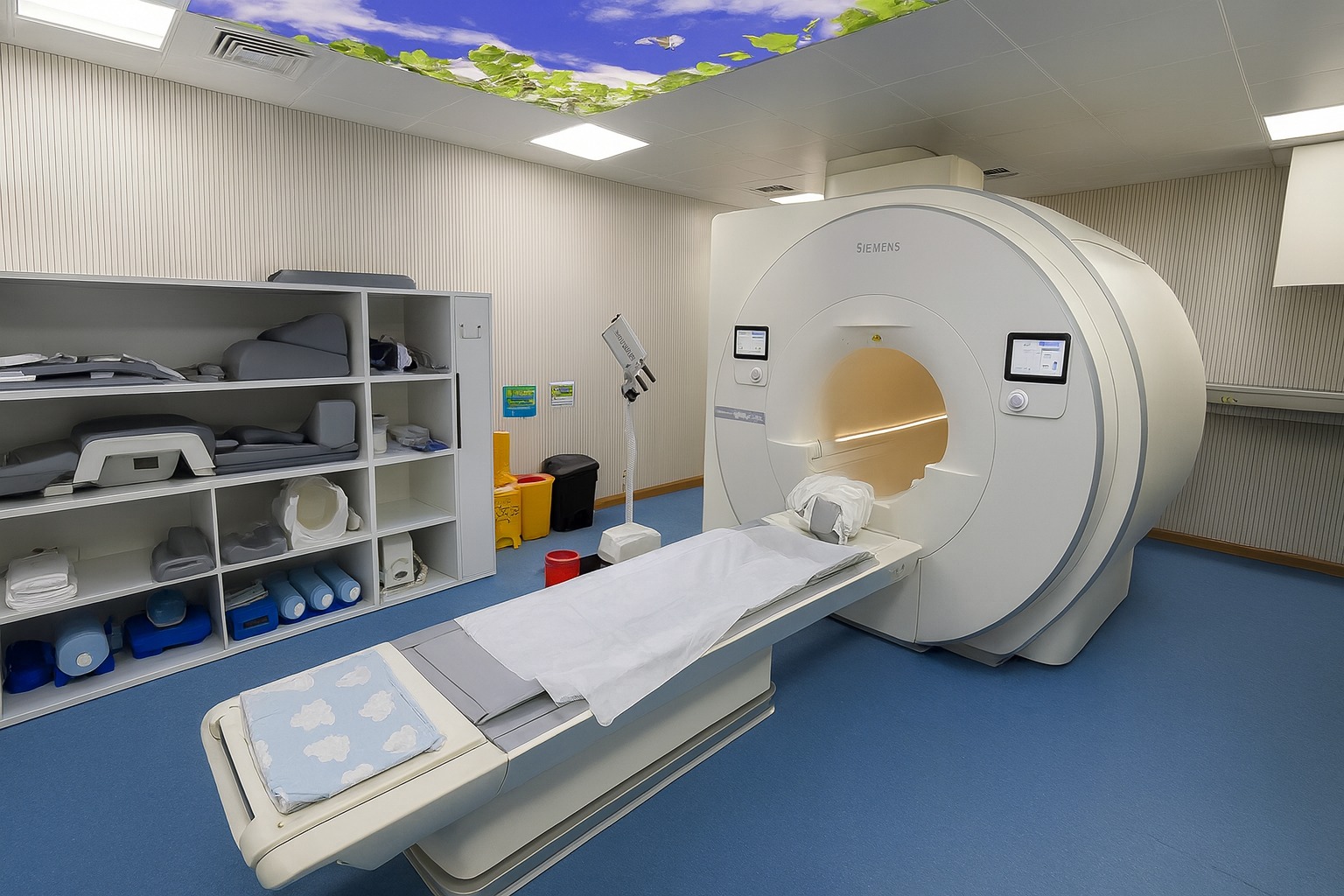
How It Works:
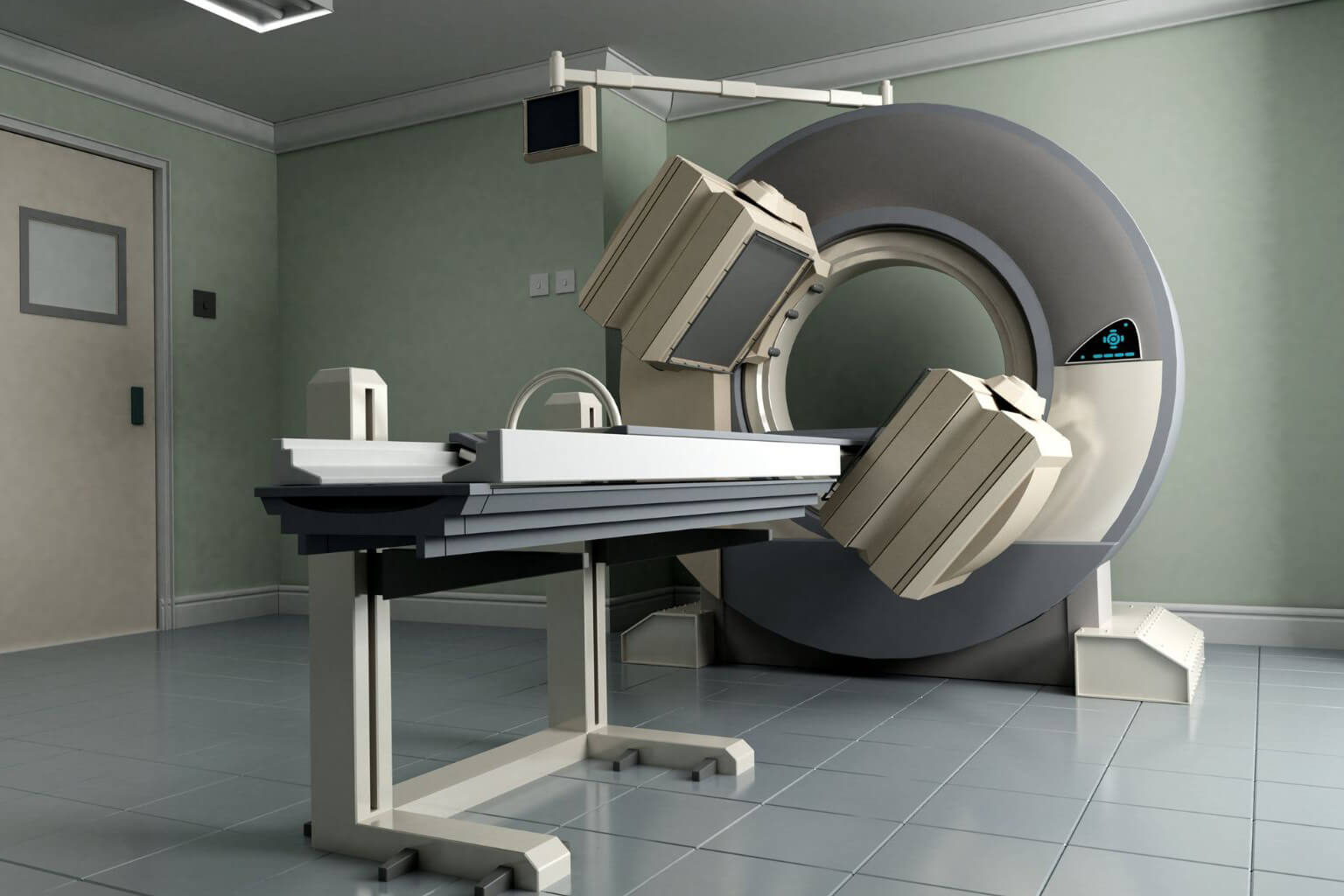
A Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography (SPECT/CT) system is a hybrid medical imaging device that combines functional (SPECT) and anatomical (CT) imaging to provide detailed 3D maps of physiological processes in the body. It is widely used in oncology, cardiology, neurology, and orthopedics.
How SPECT/CT Works:
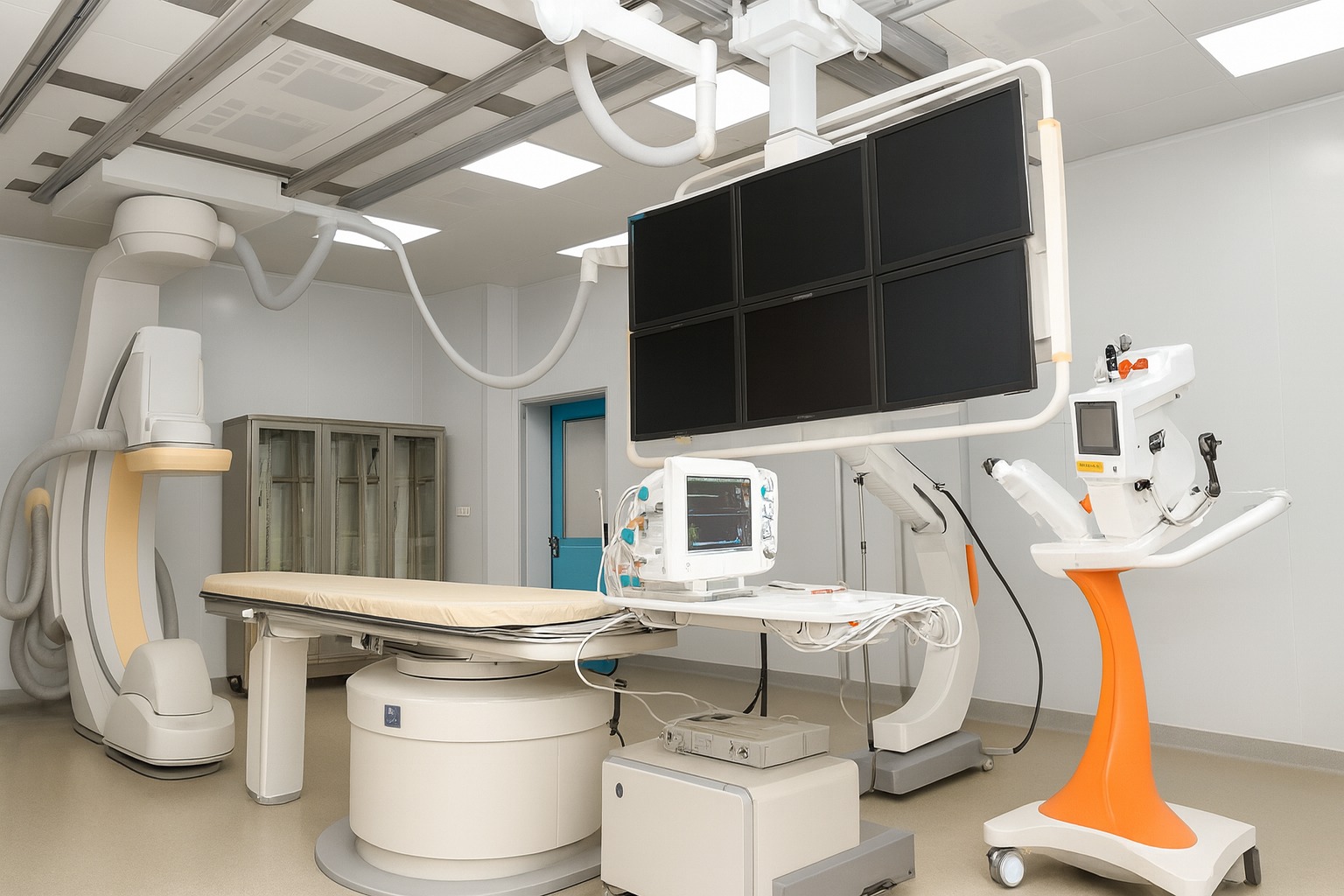
A Vascular Interventional Therapy System (Digital Subtraction Angiography, DSA) is an advanced medical imaging technology used to diagnose and treat vascular (blood vessel) diseases in real time. It combines high-resolution X-ray imaging with catheter-based minimally invasive procedures to visualize and repair blood vessels with pinpoint accuracy.
How DSA Works:
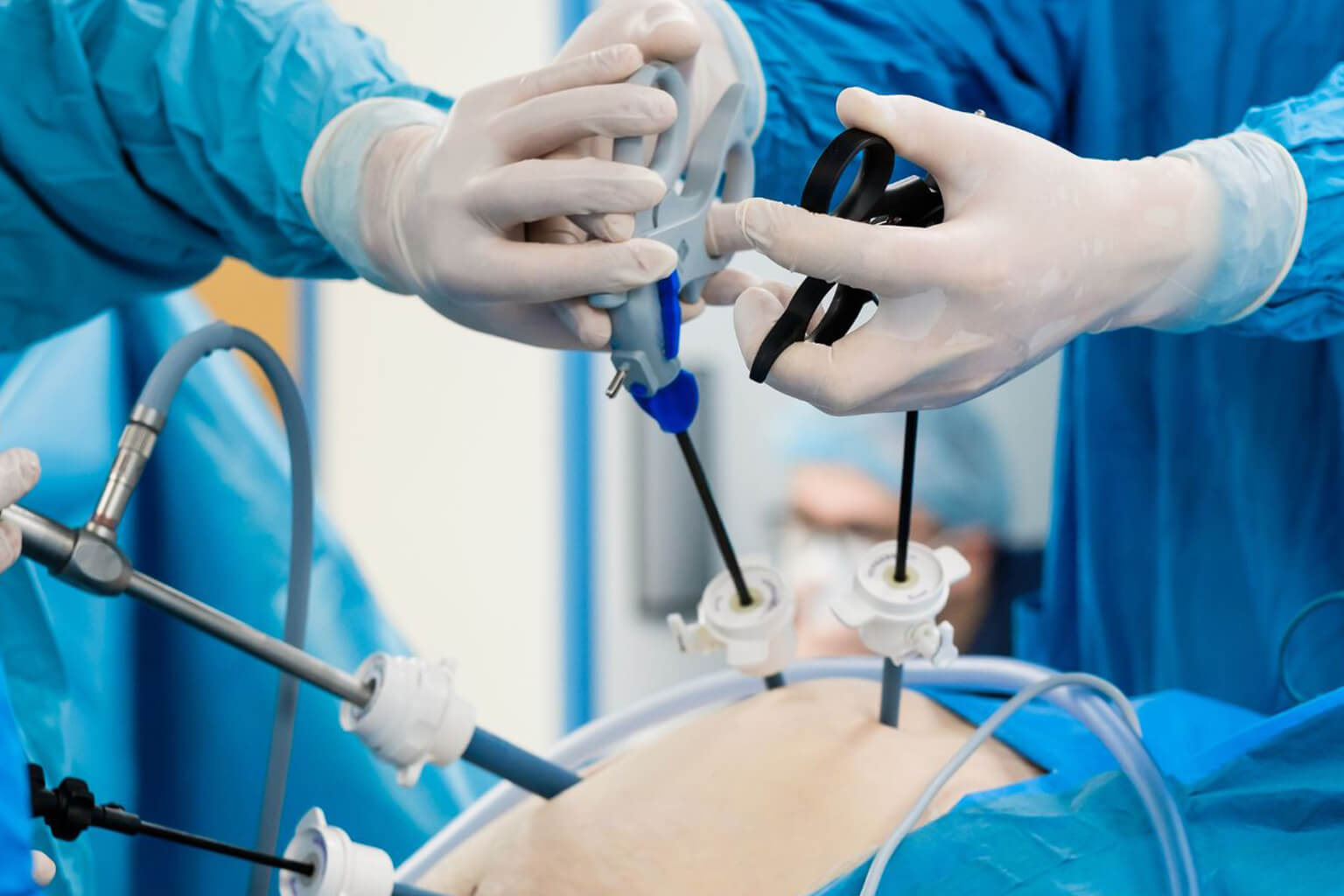
A 3D Thoracic Laparoscopic System is an advanced minimally invasive surgical platform that combines high-definition 3D visualization with specialized instruments to perform precise surgeries in the chest (thoracic cavity) through tiny incisions. It is commonly used for lung, esophageal, and mediastinal procedures.
Key Components & How It Works: